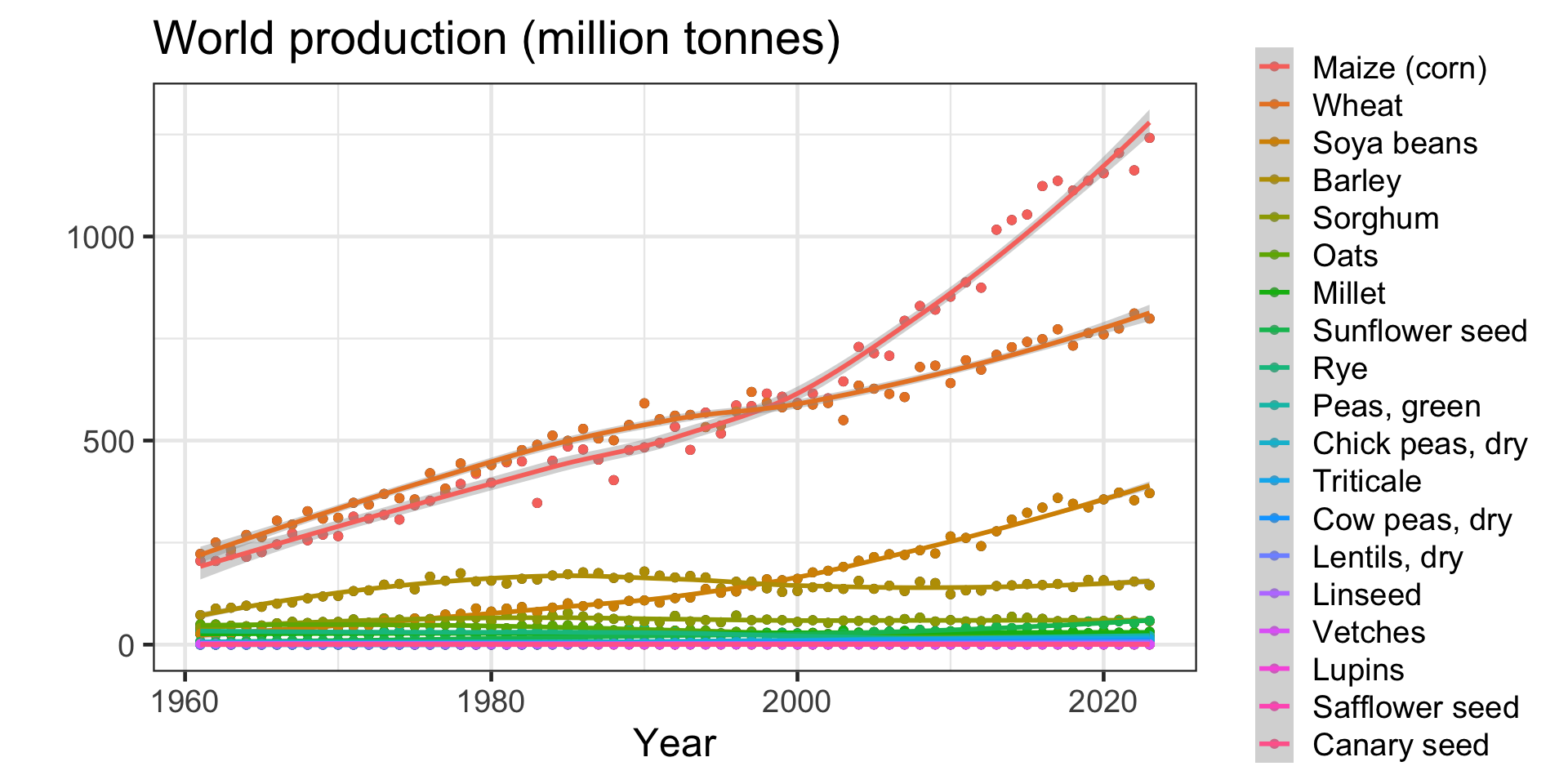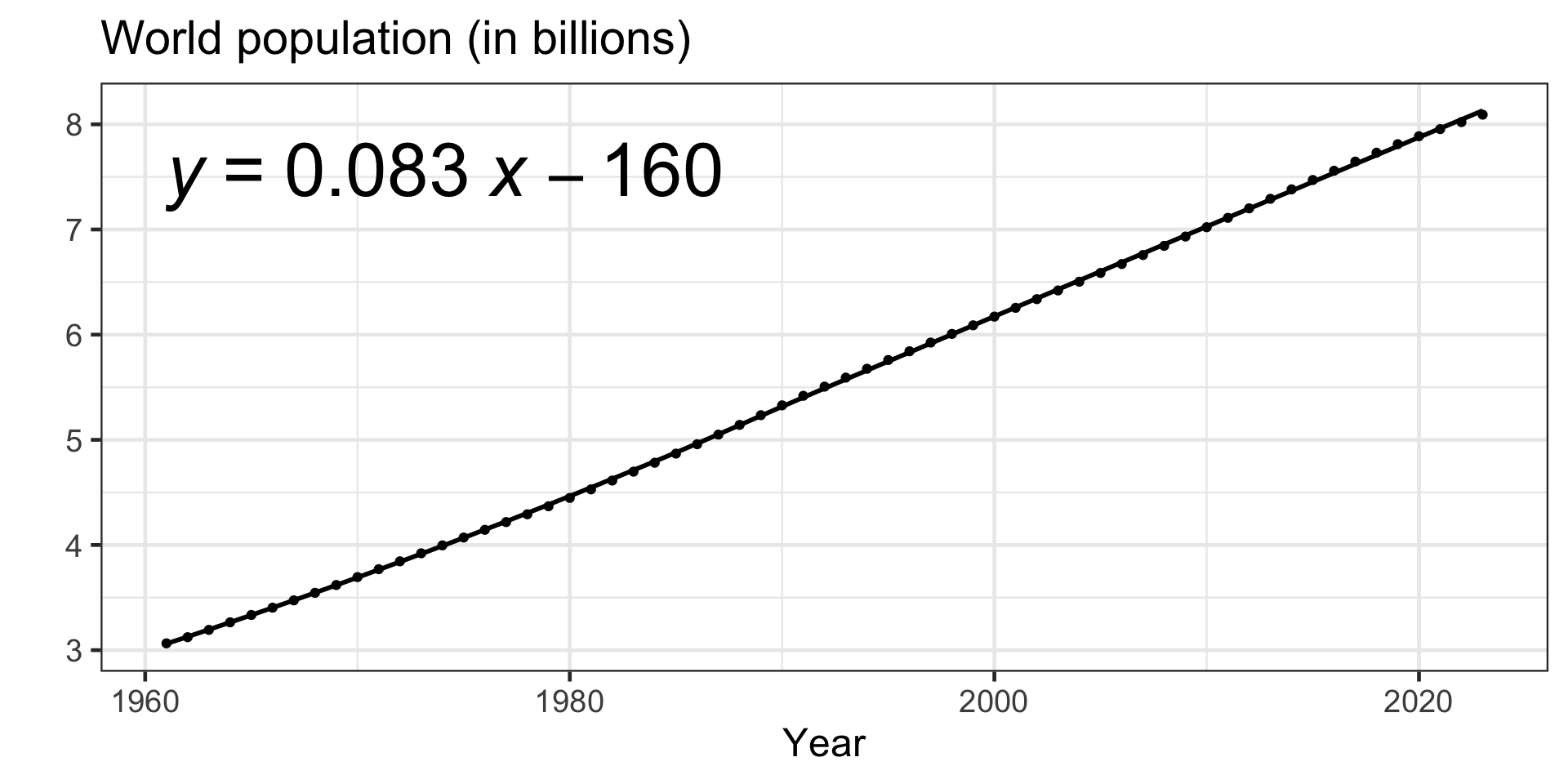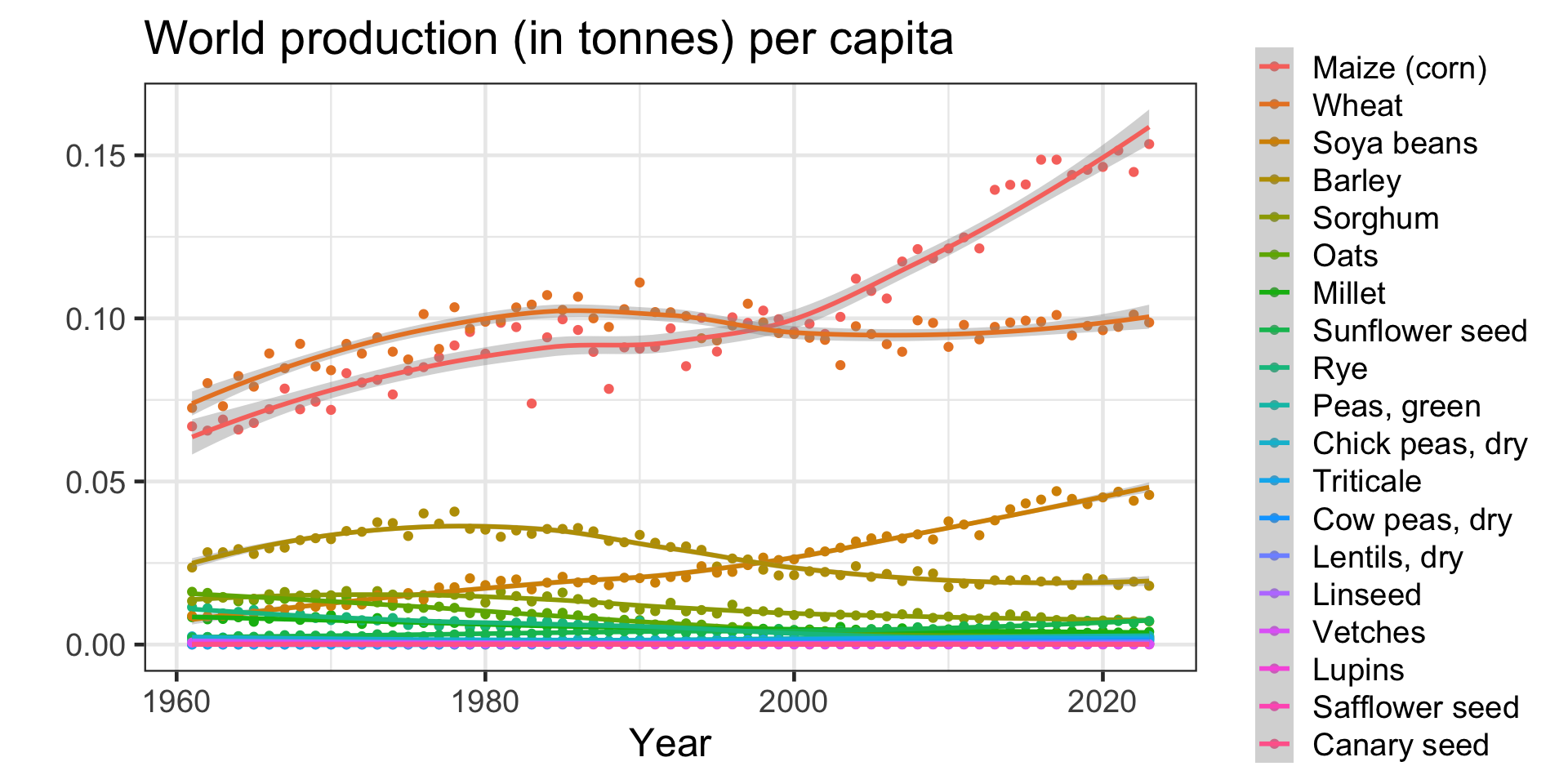
Short introduction to
selective breeding
Emi Tanaka
Australian National University
2025-07-09
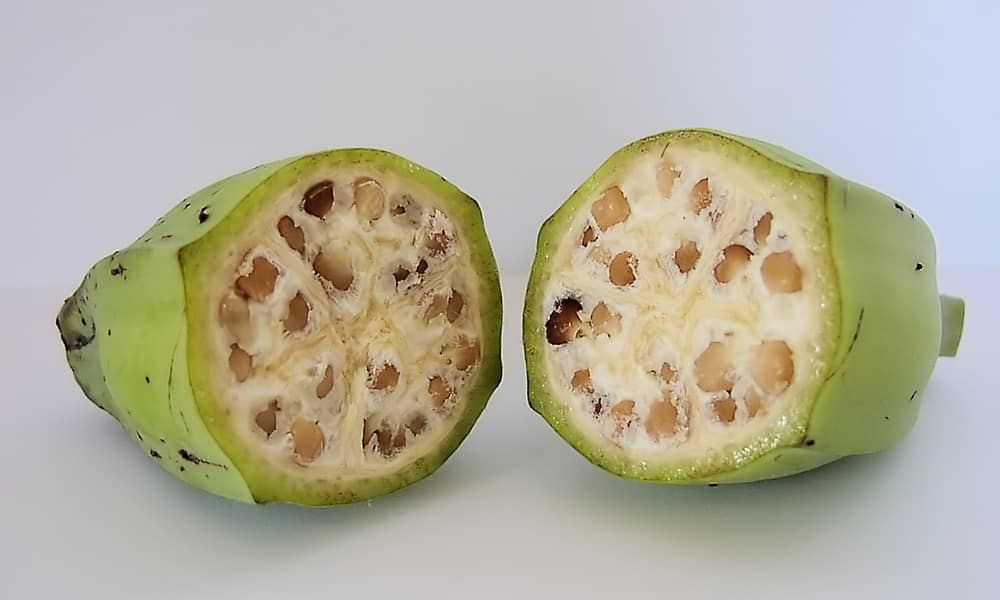
Wild vs Cultivated
Wild vs Cultivated
What is this?

Evolution of corn (maize)
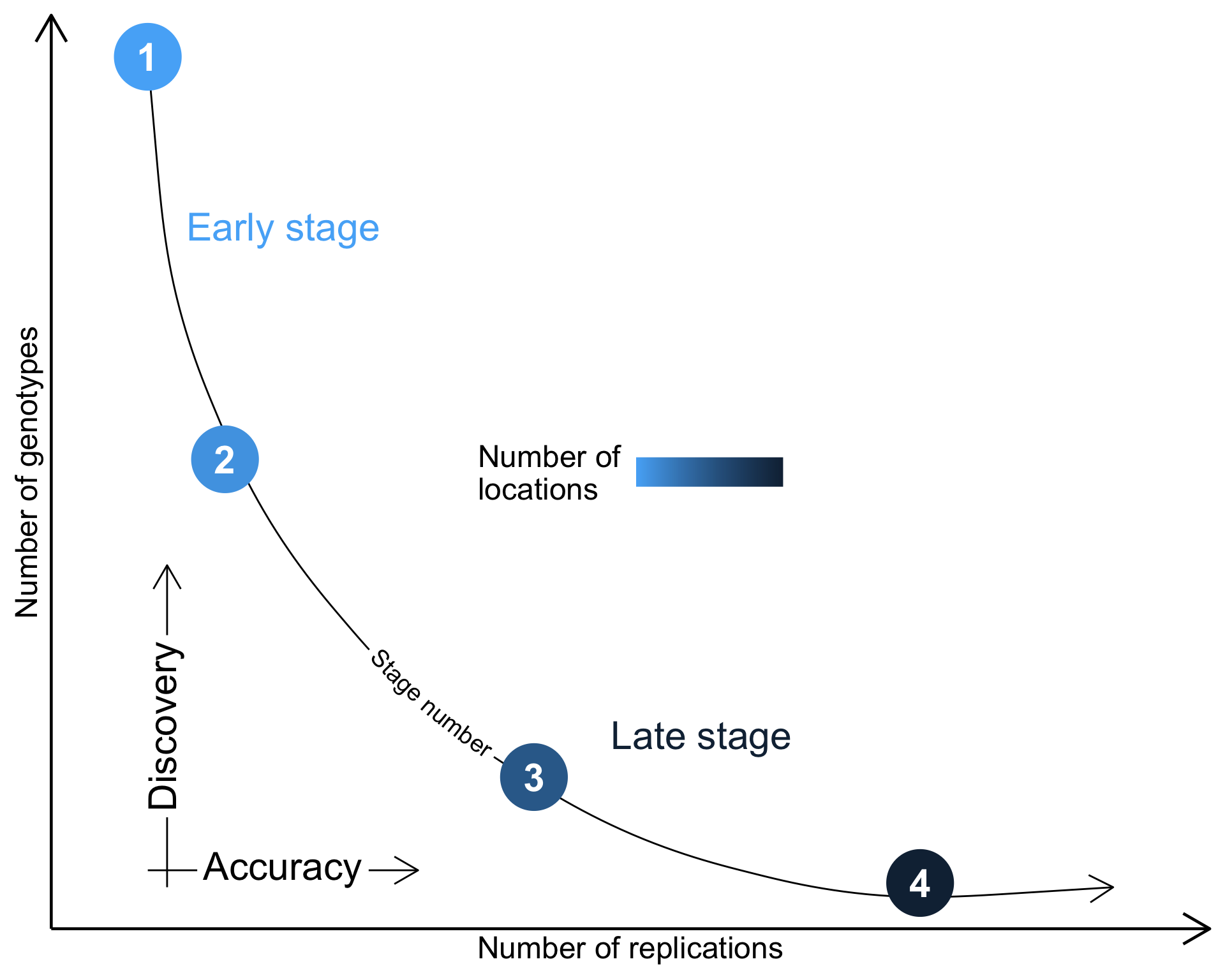
Breeding cycle
For plant breeding, the number of locations generally increase for later stages.
Why do selective breeding?
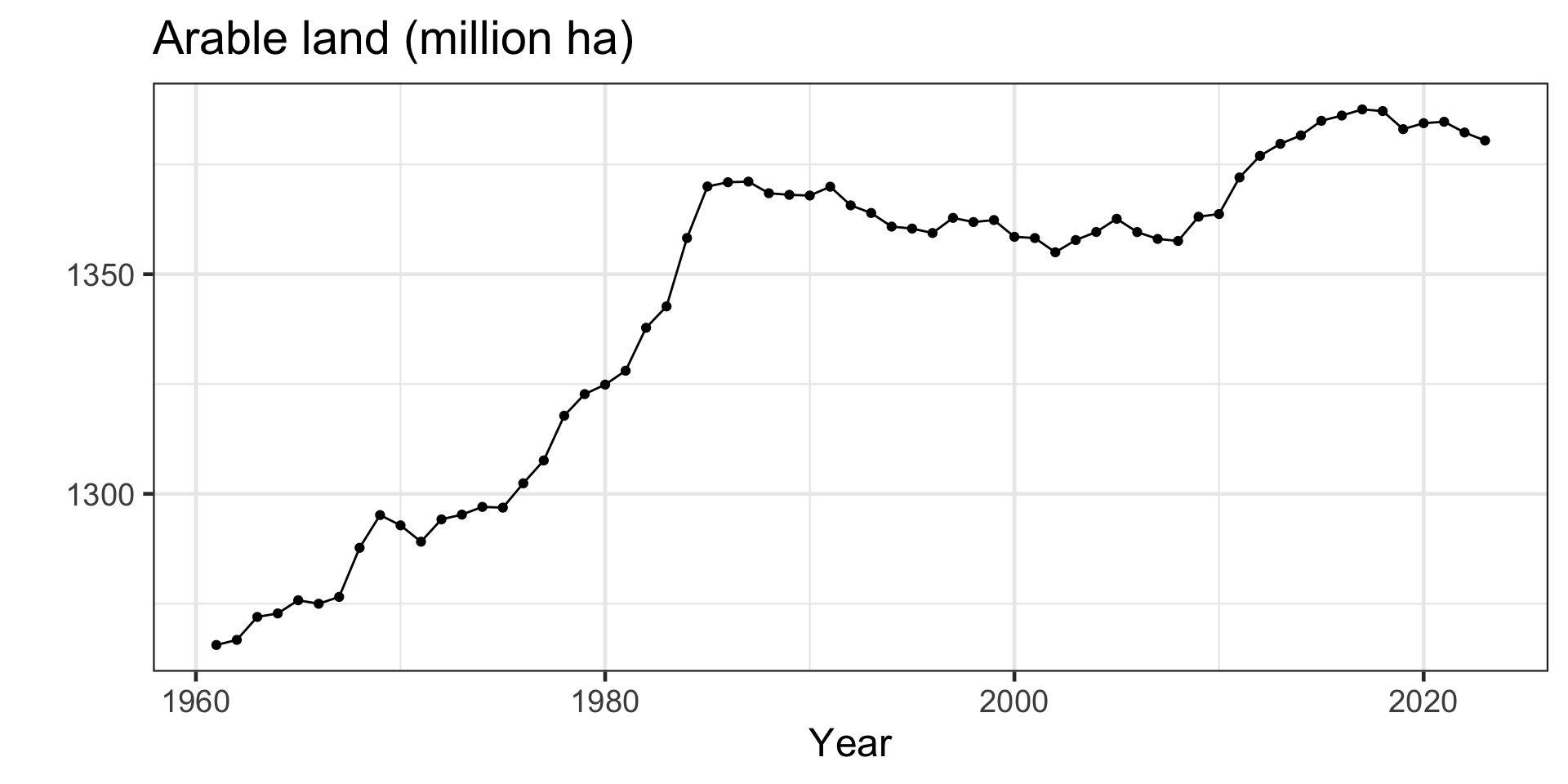
Yield = Production / Area Harvested
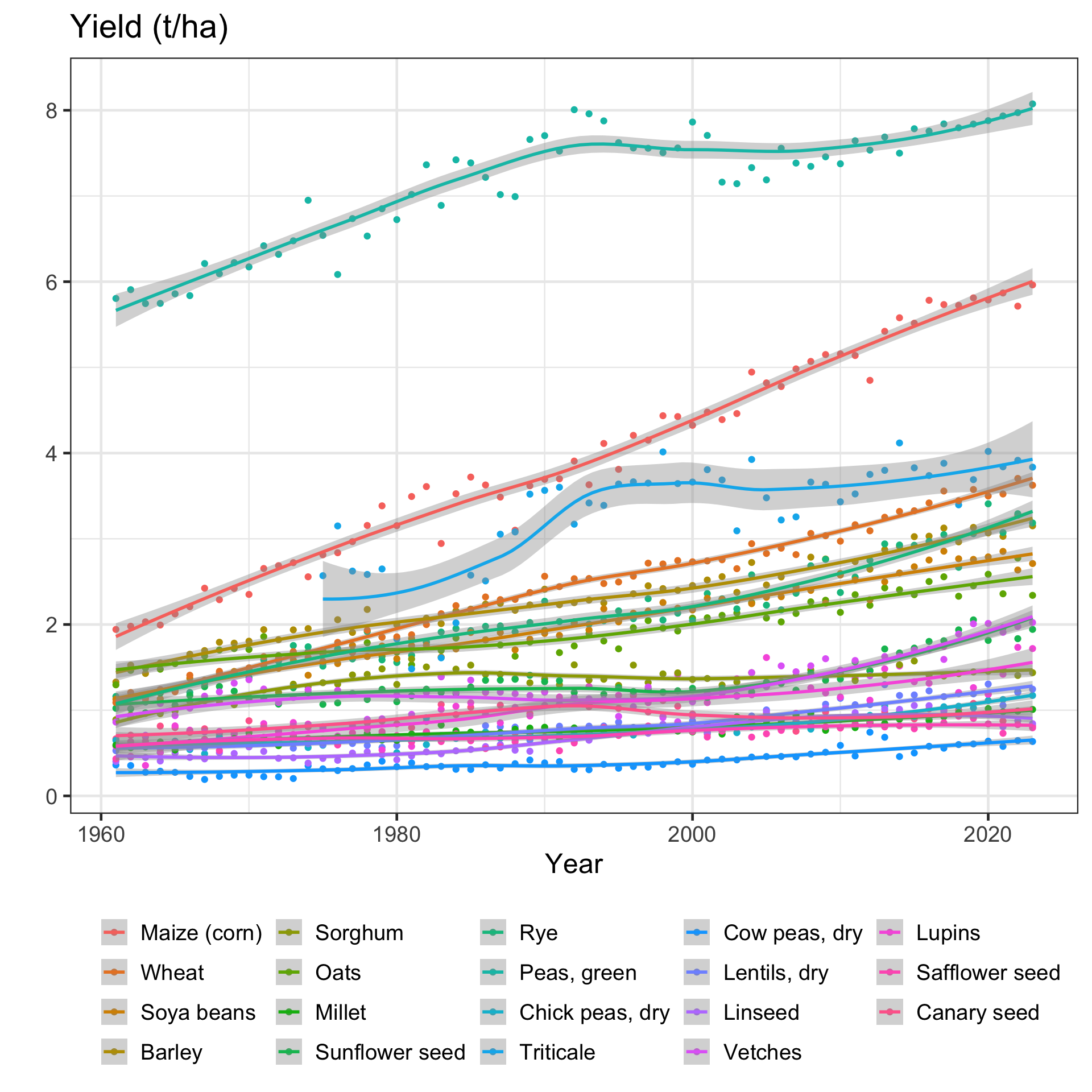
What trait to optimise?
Yield
(economic driver)
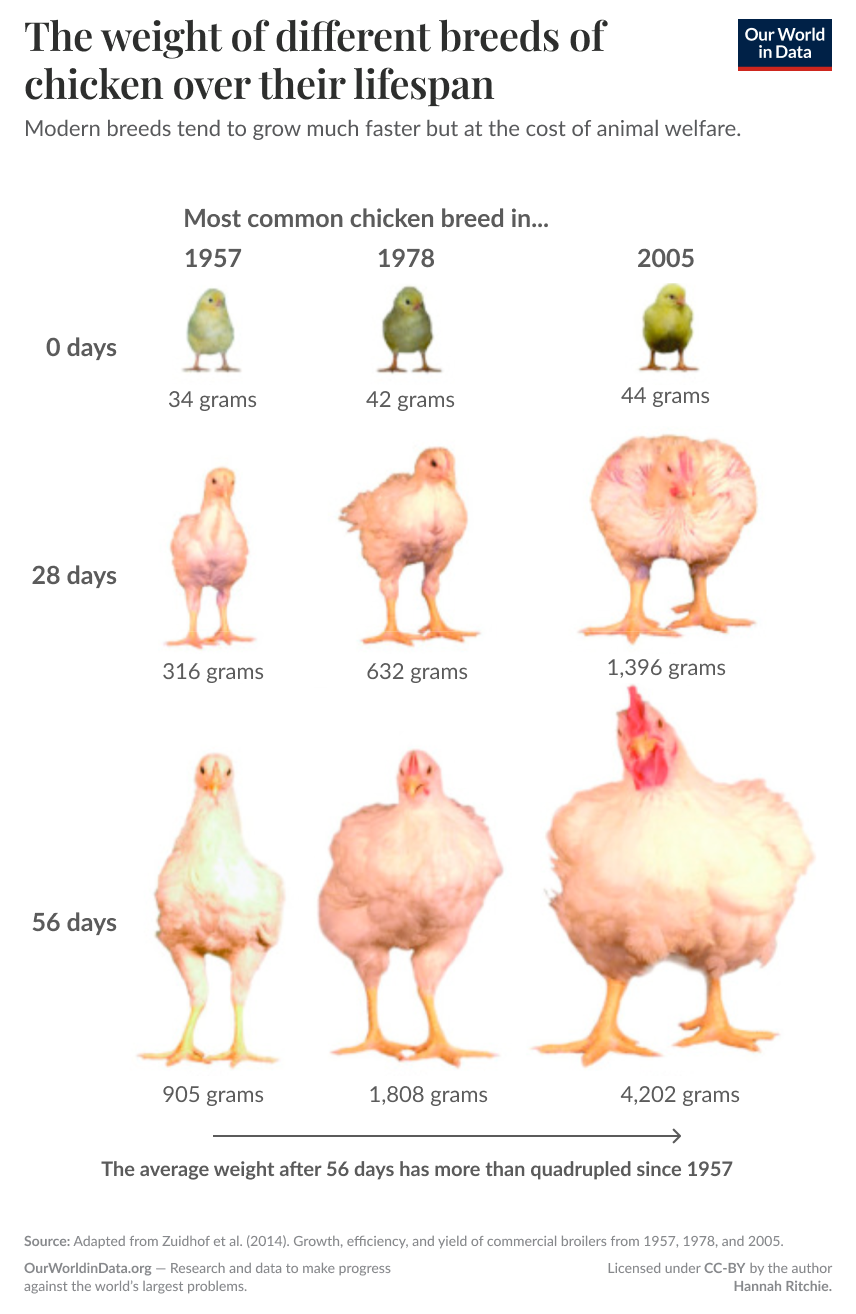

Quality traits, disease resistance, and other desirable traits.
Aim of selective breeding in a nutshell
🎯 Increase genetic gain
- Genetic gain measures improvement in the average genotype performance of a population over time due to selection for specific traits.
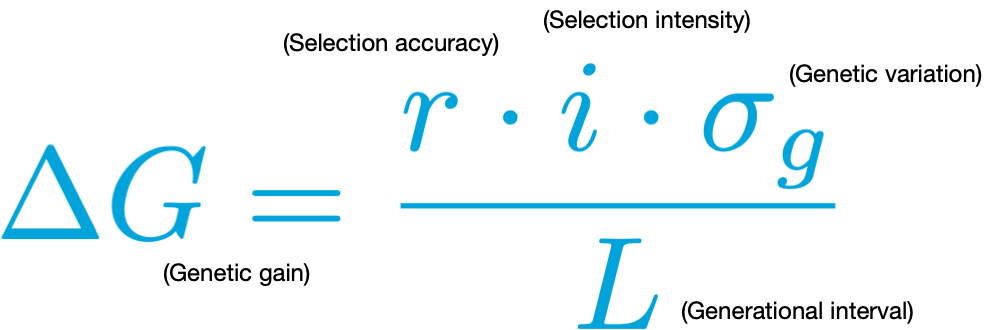
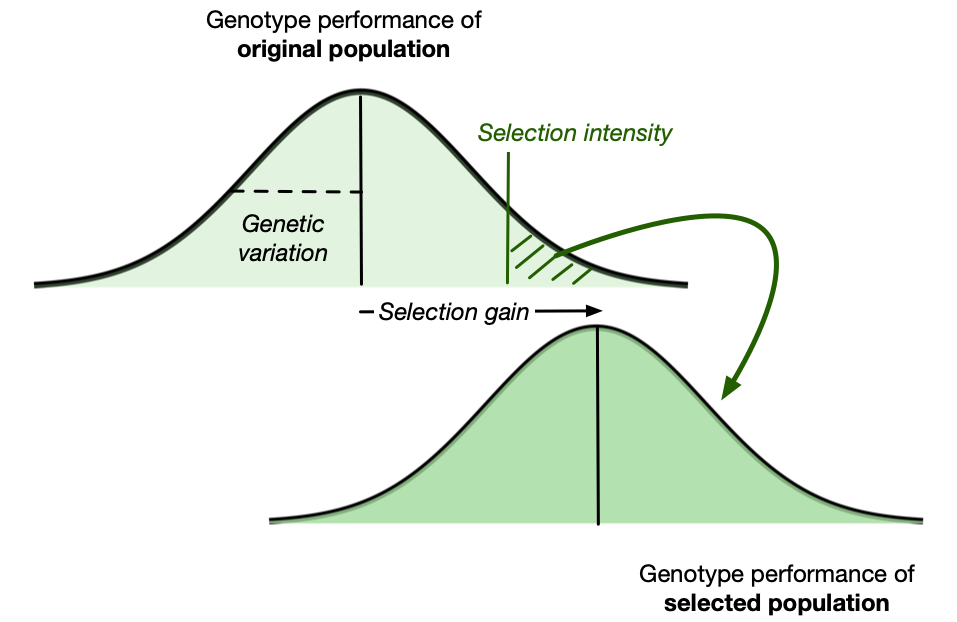
Analytical strategies for selective breeding
- Improve selection accuracy
- Use effective experimental design that separate out sources of variation for the response
- Use appropriate models to disaggregate “noise” from “signal” to get accurate estimates of breeding values
- Marker assisted selection
- Identify DNA markers related to desirable traits (e.g. disease resistance)
- Some traits are dependent only for a small number of DNA markers
- Screen candidate genotypes based on these markers
- Genomic selection
- Use a training population to estimate the additive marker effects
- Predict breeding values of candidate genotypes